- style
Web Applications
Using OAuth 2.0 for Web Applications
Accelo's OAuth 2.0 endpoints support web applications (e.g. PHP, Perl, Java, Python, Ruby, etc.). These applications are expected to keep a secret and from such, will have the ability to access Accelo's API on behalf of a user.
This document describes how to use OAuth 2.0 when accessing Accelo's API from a web application
Contents
Overview
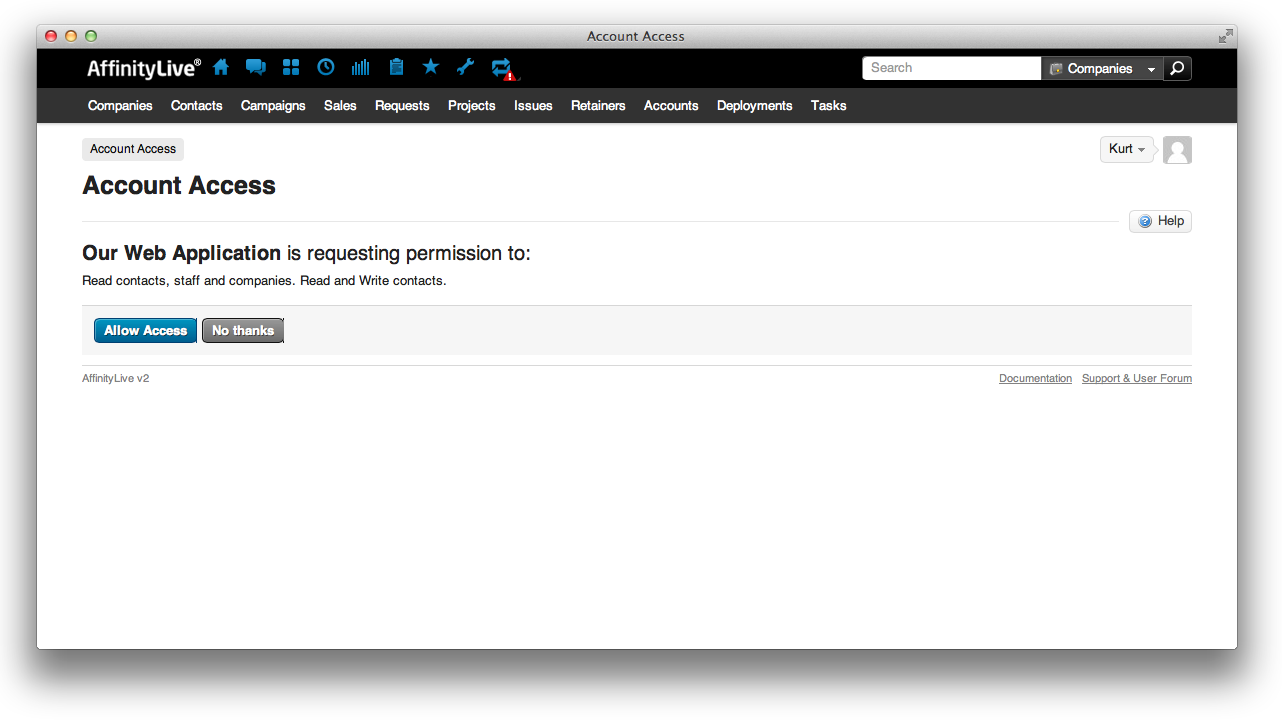
A user will be redirected by a browser to an Accelo OAuth 2.0 URL with a set of query parameters. After authentication and consent (handled by Accelo) the user will be redirected to a pre-registered URI with the result in the query string (error or authorization code).
The web application can then exchange the authorization code for an access and refresh token by presenting its client_id and client_secret along with the authorization code.
Once the application has an access token, it may use this to access the Accelo API.
Forming the URL
The OAuth 2.0 Authorization URL is oauth2/v0/authorize where SSL is required and the host is the deployment for the user requesting the access (not the web application's deployment host).
Below is a table of accepted query parameters. The optional fields are underlined.
| Parameter | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|
| client_id | The applications client id obtained from the API Control Panel. | Indicates what API application is making the request. It is a unique string allocated to your application, which can be used across multiple deployments. For example: 34ad67fa2f@hq.Accelo.com |
| response_type | code | This value must be code for web applications. |
| scope | The permissions your application requests. | A scope is used to convey what permissions your application requires when requesting permission from the end-user. Current available scopes are:
Scope resources can be any of our endpoints. For example, companies, contacts or issues. The scope can be concatenated and delimited by a comma. For example:
|
| redirect_uri | The redirect uri registered in the API Control Panel | Currently you can only attach one redirect uri to an application. Web applications must have this value. Upon user response, Accelo will redirect the user back to this URL with a response. |
| state | Any string you see fit. | The state paramater will be sent back to you as a receipt. It can be used to track a resource or to mitigate cross-site-request-reforgery attacks. For example, you may pass
|
Example URL.
https://hq.api.accelo.com/oauth2/v0/authorize? scope=read(all)& state=page_two& redirect_uri=https://app.com/oauth_callback& response_type=code& client_id=34ad67fa2f@hq.Accelo.com
Please note that the above sample url should be encoded. For example purposes it was left in plain text.
Sample of grant request given to end-user. The response of the users action will be sent to the registered redirect uri.
Handling the response
The response will be sent to the redirect_uri registered against the application or as specified in the authorization request. If the user allows access, the response will contain a code and state (if supplied in the authorization request). If the user denies access, the response will contain an error and error_descriptiondescribing why the error occurred.
The table below contains possible response parameters from an authorization request
| Response | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|
| code | An authorization code | This code can then be used when requesting an access token. This is only sent upon a success request. That is, if the user gives your application permission to access their data as specified in the scope. |
| state | The state value you sent (if any) to the authorize request. | See Forming the URL for more information regarding the state value. |
| error | Error status when there has been an error in the request | An error may occur upon a malformed request or when a user denies access. Possible error status codes appear in thestatus list. |
| error_description | Description on why error occured. | A string giving a human readable explanation on why the error may have occurred. |
Sample authorization response:
https://app.com/callback?code=frLA0s1m_D&state=1234
Sample error response:
https://app.com/callback?error=access_denied&error_description=The+user+denied+you+access.
Once you have received an authorization code from the authorization endpoint or user, you can exchange it for an access and refresh token.
The OAuth 2.0 access token URL is oauth2/v0/token where SSL is required and the host is the deployment for the user requesting the access (not the web applications deployment host).
When accessing the token endpoint it is recommended you authenticate yourself using HTTP Basic Authentication using the client_id and client_secret as username and password. The Accelo OAuth 2.0 does support sending the client_id and client_secret as query parameters as a last option.
The table below contains the token parameters.
| Parameter | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|
| grant_type | authorization_code | This is required when requesting access using an authorization grant. Note. You can send refresh_token to indicate that you are using a refresh token. In this situation, you should also send the refresh_token. |
| code | The code obtained during the authorization request. | This code was obtained during the authorization request and is used to obtain an access token. |
| redirect_uri | The redirect uri passed in the authorization request. | This must be the same as the uri passed during the authorization, failure to do so will result in an invalid_grant error. |
Here is what a request may look like, where the client id and secret are encoded using base-64.
POST /oauth2/v0/token HTTP/1.1
Host: hq.api.accelo.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Authorization: Basic {client_id}:{client_secret}
code=frLA0s1m_D&
redirect_uri=https://app.com/oauth_callback&
grant_type=authorization_code
Upon a successful request, the response contains the following fields:
| Response | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|
| access_token | string representing an access. | Credential used to access Accelo's protected resources |
| refresh_token | string representing an authorization grant | A refresh token can be used to obtain a new access token. It is similar to an authorization code in that it is a credential used to obtain an access token. |
| token_type | bearer | The type of token returned. |
| expires_in | Seconds until the token expires. | Indicates the time remaining before the token expires and becomes invalid. Upon a token expiring you can use therefresh_token to request a new access token. |
Accessing the resource
Once the application has obtained an access token, it can use it to access Accelo's Resource endpoints by including it in either a _bearer_token query parameter or as a (preferred method) HTTP Authorization: Bearer header.
Sample accessing a company resource using access token in query:
GET https://hq.api.accelo.com/api/v0/companies/1?_bearer_token=frLA0s1m_D
Sample using the preferred Authorization header method:
GET /api/v0/companies/1 HTTP/1.1 Host: hq.api.accelo.com Authorization: Bearer frLA0s1m_D
References and additional reading